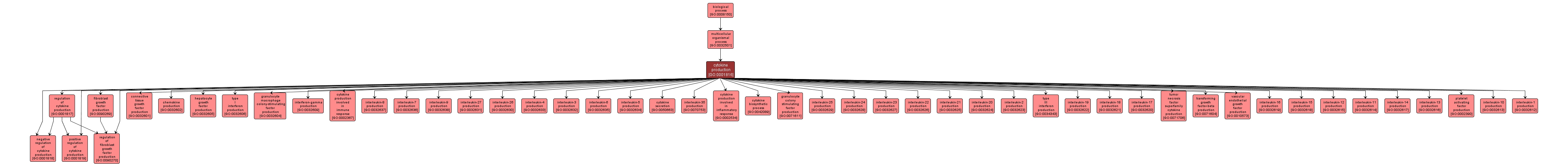
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cytokine production |
| Acc: |
GO:0001816 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The appearance of a cytokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|