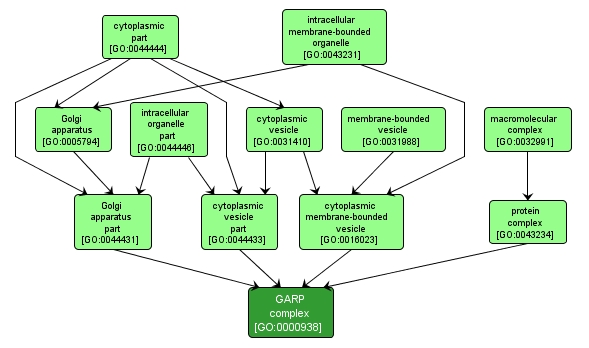
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
GARP complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0000938 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A quatrefoil tethering complex required for retrograde traffic from the early endosome back to the late Golgi and biogenesis of cytoplasmic vesicles. |
Synonyms:
- Vps fifty three tethering complex
- VFT tethering complex
- Golgi associated retrograde protein complex
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|