GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
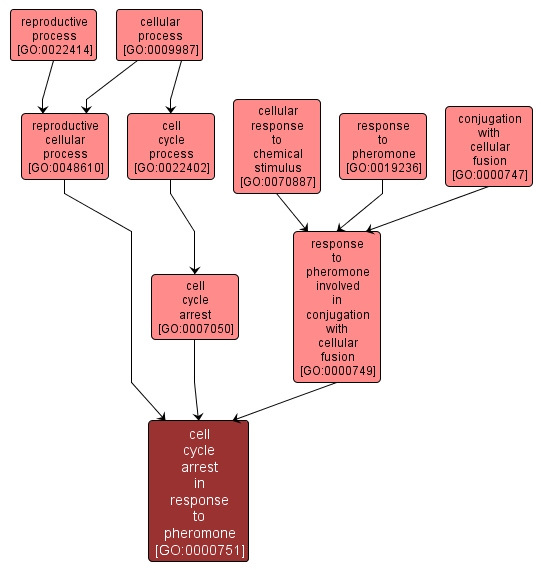
cell cycle arrest in response to pheromone |
| Acc: |
GO:0000751 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which the cell cycle is halted during one of the normal phases (G1, S, G2, M) as a result of a pheromone stimulus. An example of this process is found in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|