GO TERM SUMMARY
|
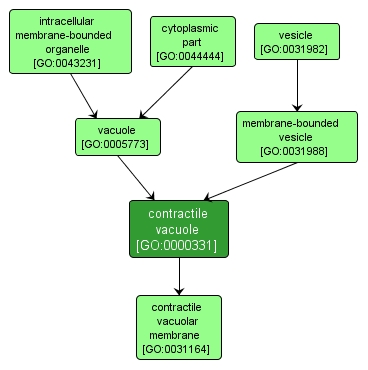
| Name: |
contractile vacuole |
| Acc: |
GO:0000331 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A specialized vacuole of eukaryotic cells, especially Protozoa, that fills with water from the cytoplasm and then discharges this externally by the opening of contractile vacuole pores. Its function is probably osmoregulatory. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|