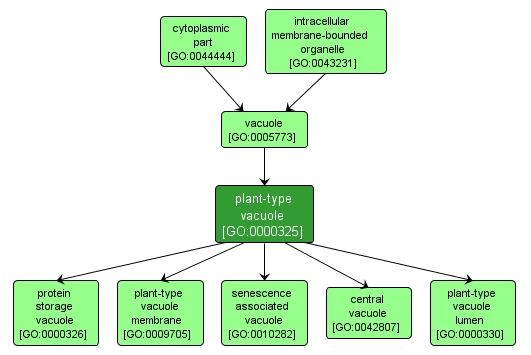
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
plant-type vacuole |
| Acc: |
GO:0000325 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A closed structure that is completely surrounded by a unit membrane, contains liquid, and retains the same shape regardless of cell cycle phase. An example of this structure is found in Arabidopsis thaliana. |
Synonyms:
- vacuole, cell cycle-independent morphology
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|