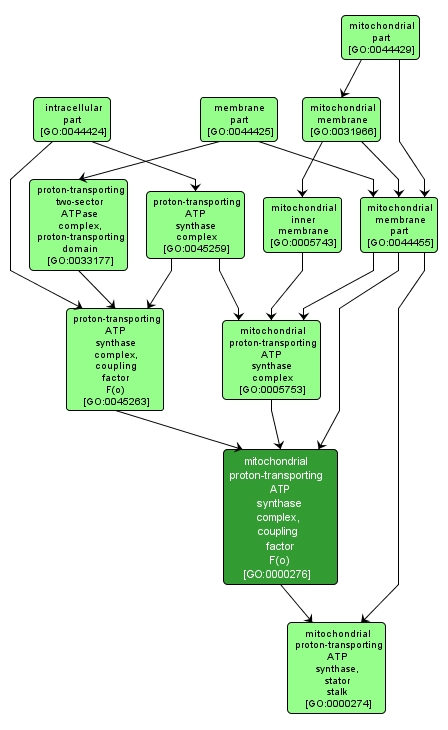
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex, coupling factor F(o) |
| Acc: |
GO:0000276 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
All non-F1 subunits of the mitochondrial hydrogen-transporting ATP synthase, including integral and peripheral mitochondrial inner membrane proteins. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|