| Desc: |
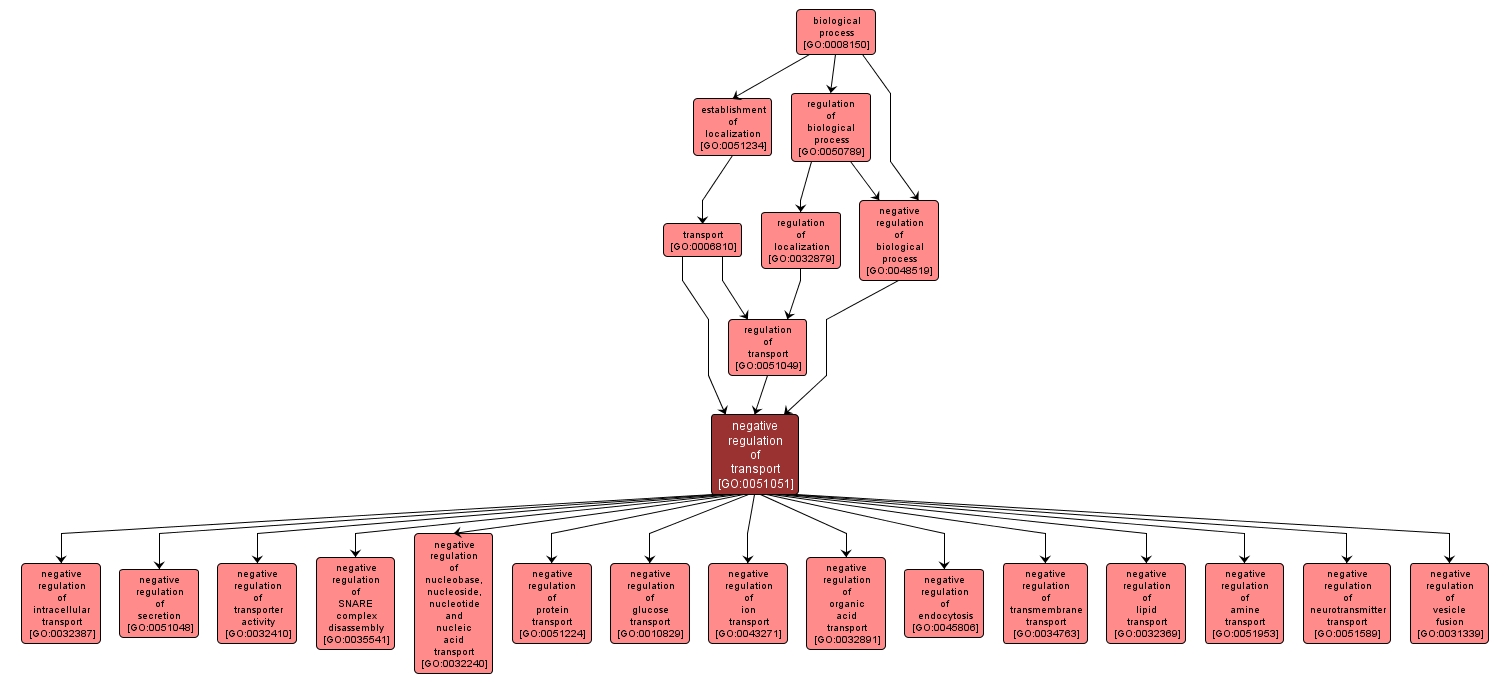
Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of substances (such as macromolecules, small molecules, ions) into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. |