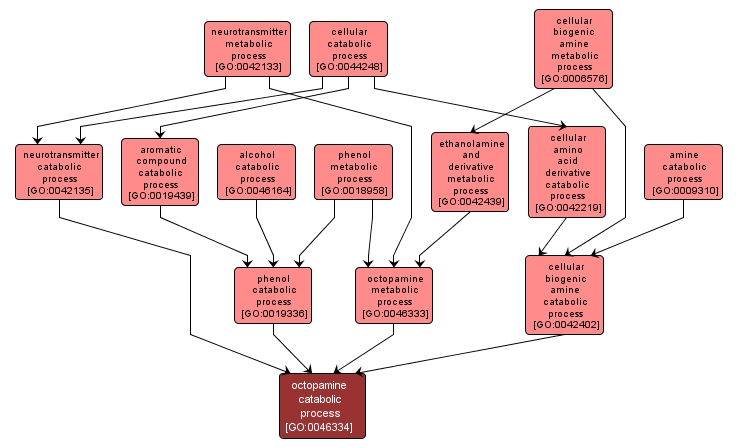
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
octopamine catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0046334 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of octopamine, 1-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-2-aminoethanol. The D enantiomer is about one-tenth as active as norepihephrine and is found in the salivary glands of Octopus and Eledone species. |
Synonyms:
- octopamine breakdown
- octopamine catabolism
- octopamine degradation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|