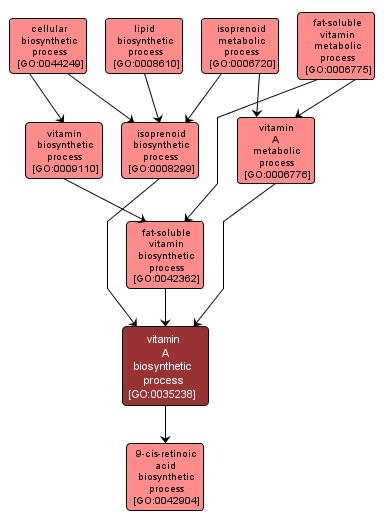
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
vitamin A biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0035238 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of any of the vitamin A compounds, retinol, retinal (retinaldehyde) and retinoic acid. Animals can not synthesize vitamin A de novo, but form it through oxidative cleavage of carotenoids. |
Synonyms:
- vitamin A synthesis
- vitamin A biosynthesis
- vitamin A anabolism
- vitamin A formation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|