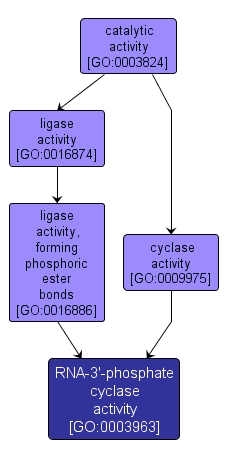
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
RNA-3'-phosphate cyclase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0003963 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + RNA 3'-terminal-phosphate = AMP + diphosphate + RNA terminal-2',3'-cyclic-phosphate. |
Synonyms:
- RNA-3'-phosphate:RNA ligase (cyclizing, AMP-forming)
- RNA 3'-terminal phosphate cyclase activity
- RNA cyclase activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|